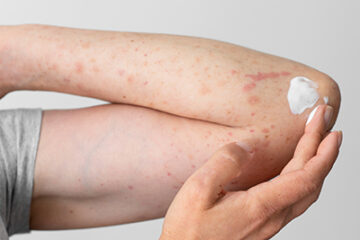
Researchers at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City have uncovered a potential method for slowing skin fibrosis for patients with scleroderma.
Scleroderma is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation in fibrotic tissue below the skin. The disease can also affect the lungs, blood vessels, and other organs in the body. Treatment options are typically limited.
In a study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers used stem cells called adipose-derived stromal cells, or ADSCs, to test how the characteristic erosion of skin occurs during scleroderma.
During the study, the authors found the ADSCs depend on a compound released by immune cells known as dendritic cells to survive beneath the skin. By stimulating the compound with antibodies, researchers were able to replenish lost ADSCs, suggesting the damage associated with scleroderma can be reversed.
“Injecting ADSCs is being tried in scleroderma; the possibility of stimulating the lymphotoxin B pathway to increase the survival of these stem cells is very exciting,” lead researcher Theresa Lu said in a press release. “By uncovering these mechanisms and targeting them with treatments, perhaps one day we can better treat the disease.”
Lu believes a similar approach can be used to target stem cells in other conditions such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. The research team hopes to replicate their experiment using human cells in the future.
“Improving ADSC therapy would be a major benefit to the field of rheumatology and to patients suffering from scleroderma,” she added.
[Source:-UPI]